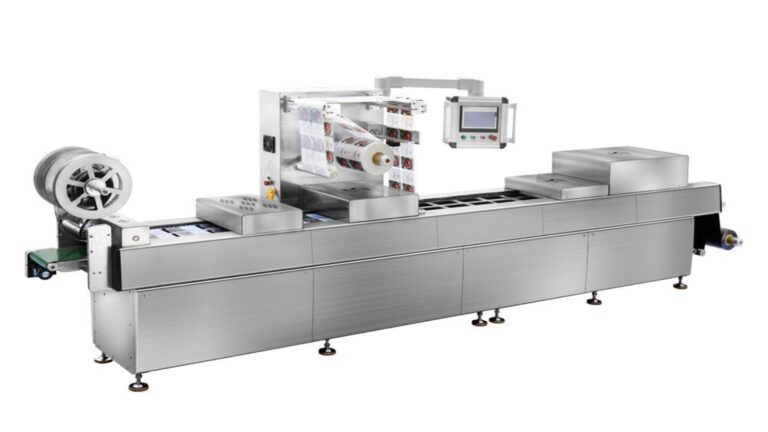
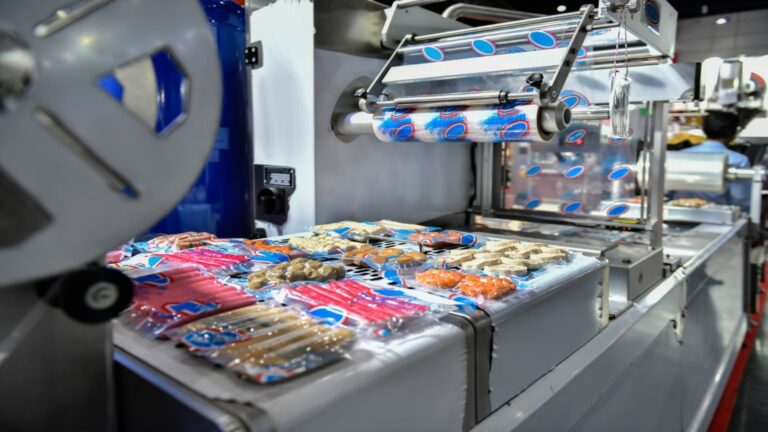
Vacuum Forming: A Comprehensive Guide to Thermoforming Plastic Sheets
What is Vacuum Forming?
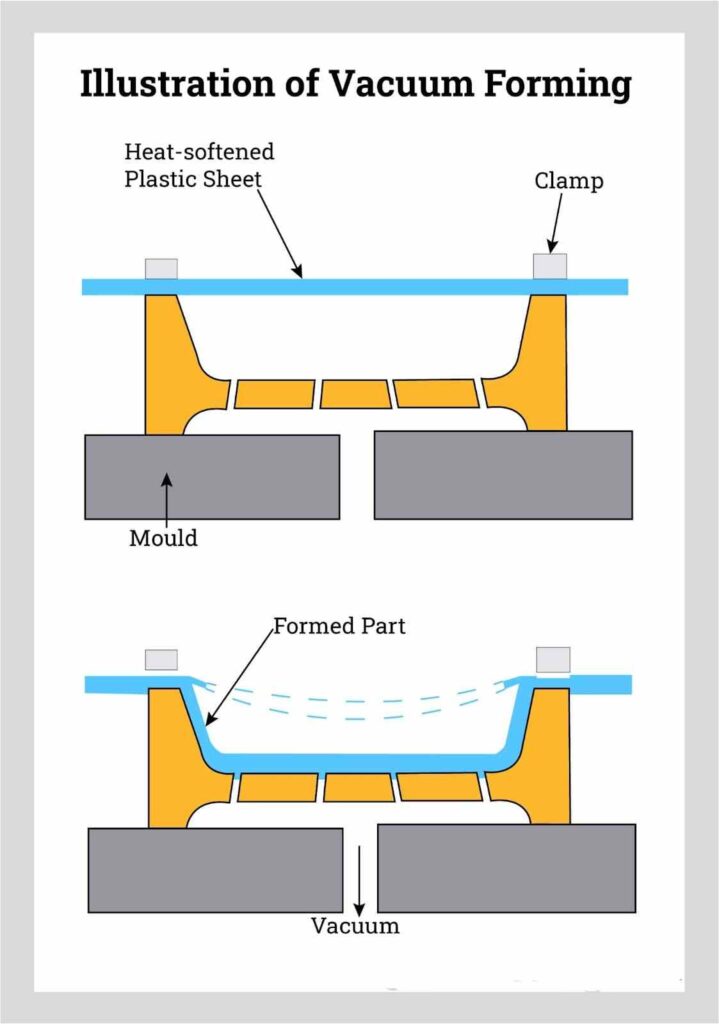
How Does the Vacuum Forming Process Work?
1. Mold Preparation
- Prototyping/Small Batches: Molds made from wood, foam, or 3D-printed plastic (cost-effective, quick to produce).
- Medium-to-High Volume: Molds made from aluminum or steel (durable, heat-resistant, and suitable for repeated use).
2. Material Selection & Cutting
- PVC: Affordable, versatile, and ideal for signage, packaging, and consumer goods.
- Acrylic (PMMA): Transparent, scratch-resistant, and used for displays, lighting fixtures, and decorative panels.
- ABS: Durable, impact-resistant, and suitable for industrial parts, cosplay props, and automotive components.
- PETG: Food-safe, recyclable, and used for packaging, medical devices, and retail displays.
- PP/PS: Lightweight, cost-effective, and common in disposable packaging and consumer products.
3. Heating the Plastic Sheet
- Uniformity: Even heating ensures the sheet softens consistently, preventing uneven stretching or thinning.
- Temperature Control: Overheating can cause the sheet to degrade or bubble; underheating results in incomplete forming.
- Heating Time: Varies by material thickness (thin sheets: 30–60 seconds; thick sheets: 2–5 minutes).
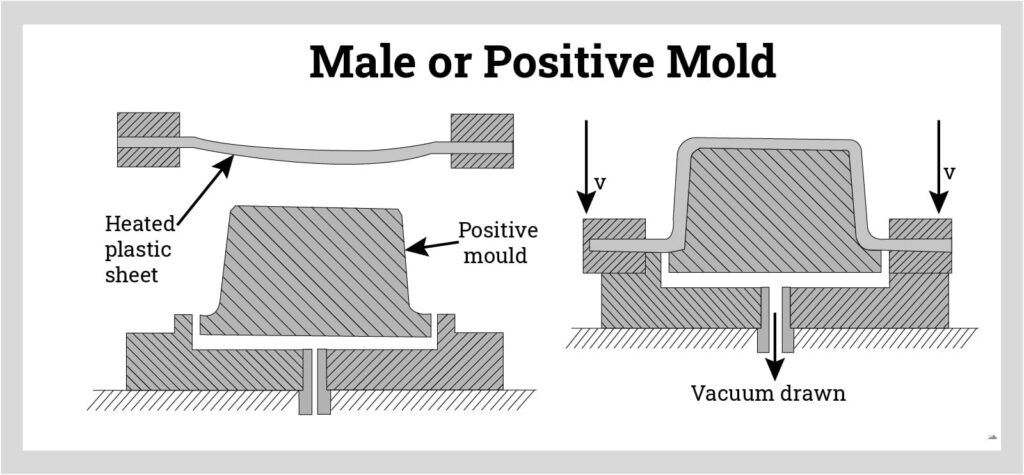
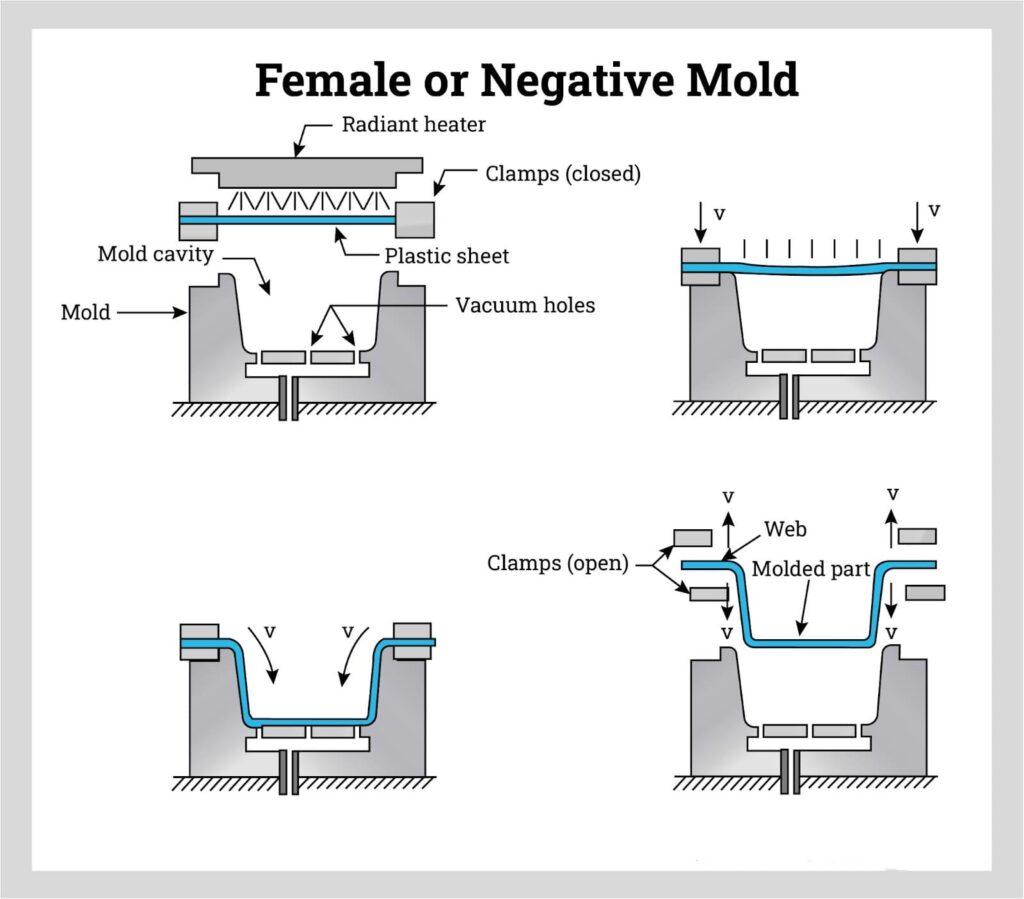
4. Forming the Plastic
- Plug Assist: A solid plug pushes the sheet into the mold before vacuum is applied, ensuring even stretching.
- Pressure Forming: Combining vacuum pressure with positive air pressure (from above the sheet) for tighter mold adherence.
5. Cooling & Solidification
- Air Cooling: Blowing ambient or chilled air over the part (fast, cost-effective for most applications).
- Water Cooling: Molds with built-in water channels for faster cooling (ideal for high-volume production).
6. Trimming & Finishing
- Sanding or polishing to smooth edges.
- Drilling holes for assembly.
- Painting, printing, or laminating for aesthetic or functional purposes.
Types of Vacuum Forming Machines
1. Manual Vacuum Forming Machines
- Best For: Prototyping, small workshops, and low-volume production (e.g., DIY cosplay props, custom home decor).
- Features: Manual clamping, heating, and mold positioning—affordable and easy to operate.
- Limitations: Limited to small-to-medium sized parts; slower production speed.
2. Semi-Automatic Vacuum Forming Machines
- Best For: Medium-volume production, small businesses, and industrial workshops.
- Features: Automated heating and vacuum cycles; manual mold loading/unloading.
- Advantages: Faster than manual machines; consistent results; suitable for large-format parts (e.g., advertising billboards, automotive interior panels).
3. Fully Automatic Vacuum Forming Machines
- Best For: High-volume production, industrial manufacturing, and precision parts (e.g., medical devices, packaging).
- Features: Automated sheet feeding, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and stacking.
- Advantages: High throughput (hundreds to thousands of parts per hour); minimal operator intervention; tight dimensional control.
4. Large-Format Vacuum Forming Machines
- Best For: Big thermoforming pieces (e.g., large signs, architectural panels, industrial molds).
- Features: Extended worktables (up to 12’x24’ or larger); high-power heating systems; deep forming capabilities.
- Example: The BSX-1224 Vacuum Forming Machine—designed for large-scale 3D thermoforming of Acrylic, ABS, and PVC, with adjustable material sizes and fast uniform heating.
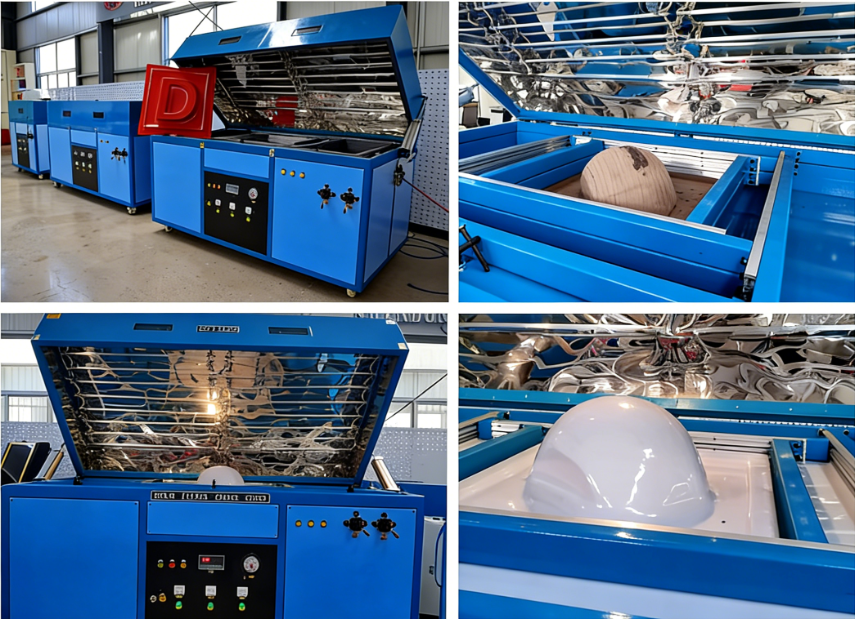

Key Advantages of Vacuum Forming
1. Cost-Effective Tooling & Production
- Mold costs are 50–90% lower than injection molding (especially for large or custom parts).
- Low setup costs make it feasible for prototyping and small-batch runs.
- Material waste is minimal (scrap can often be recycled).
2. Versatility in Design & Materials
- Accommodates complex shapes, deep cavities, and intricate details.
- Works with a wide range of thermoplastics (PVC, Acrylic, ABS, PETG, etc.).
- Suitable for small parts (e.g., electronic enclosures) and large-format products (e.g., 10’+ billboards).
3. Efficiency & Speed
- Quick mold setup (prototyping molds can be ready in days, not weeks).
- Fast production cycles (especially with automatic machines).
- Ideal for time-sensitive projects or short lead times.
4. Durability & Quality
- Produces parts with consistent thickness, strength, and surface finish.
- Thermoplastics offer excellent durability, impact resistance, and chemical resistance (depending on material).
- Suitable for food-safe, medical-grade, and industrial-grade applications.

Common Applications of Vacuum Forming
1. Advertising & Signage
- Acrylic lettering and logos.
- Large-format billboards and illuminated signs.
- Retail displays and point-of-purchase (POP) stands.
2. Packaging
- Blister packs for electronics, toys, and medical devices.
- Food trays (e.g., deli containers, fast-food packaging).
- Protective packaging for industrial parts.
3. Automotive & Transportation
- Interior panels (door panels, dashboard trim).
- Exterior components (bumpers, fender flares).
- Cargo liners and storage solutions.
4. Cosplay & Entertainment
- Custom props (armor, weapons, masks).
- Costume accessories and set pieces for film/TV.
5. Home Decor & Furniture
- Decorative panels and wall art.
- Custom storage solutions (shelves, bins).
- Furniture components (chair backs, table tops).
6. Medical & Healthcare
- Disposable medical devices (trays, housings).
- Medical equipment enclosures (MRI/CT scan components).
- Food-safe and sterile packaging.
7. Industrial & Manufacturing
- Industrial molds and templates.
- Machine guards and covers.
- Architectural panels and building materials.

How to Choose the Right Vacuum Forming Machine
1. Production Volume
- Small batches/prototyping: Manual or semi-automatic machine.
- Medium-to-high volume: Semi-automatic or fully automatic machine.
2. Part Size & Dimensions
- Small parts (≤24”x24”): Compact manual machine.
- Large parts (≥48”x48”): Large-format semi-automatic or automatic machine (e.g., BSX-1224).
3. Material Type & Thickness
- Thin sheets (≤0.125”): Standard heating system.
- Thick sheets (≥0.25”): High-power heating system with extended heating time.
- Specialized materials (e.g., medical-grade PETG): Machine with precise temperature control.
4. Precision Requirements
- High precision (e.g., medical devices): Automatic machine with digital controls.
- General use (e.g., signage): Semi-automatic machine with basic controls.
5. Budget & ROI
- Startups/small businesses: Affordable manual or semi-automatic machine.
- Industrial manufacturers: Invest in fully automatic machines for long-term efficiency.
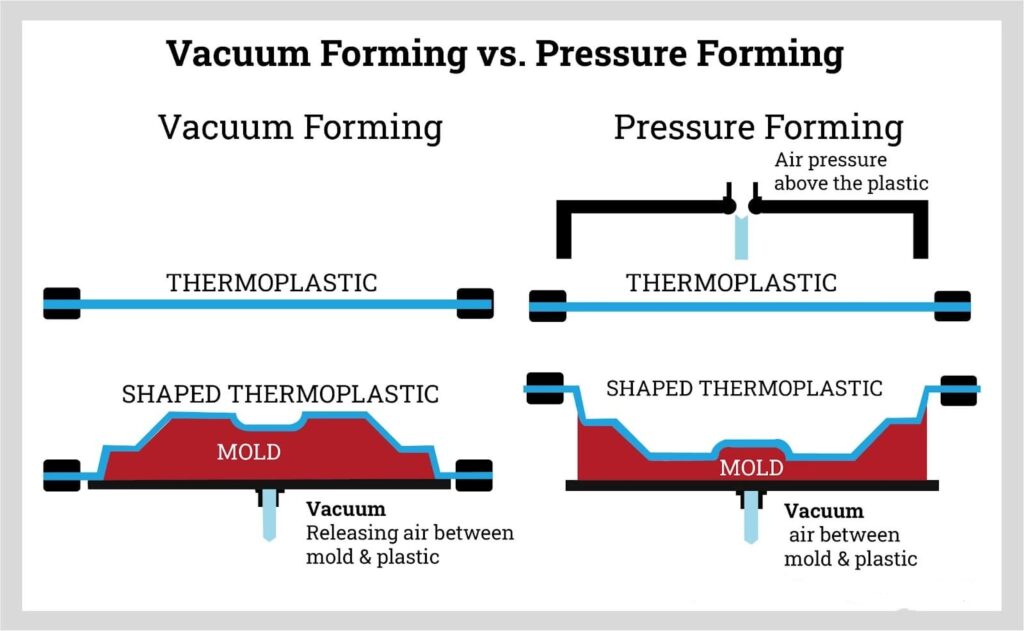
Vacuum Forming vs. Other Thermoforming Processes
|
Process
|
Key Difference
|
Best For
|
|
Vacuum Forming
|
Uses only vacuum pressure to shape plastic
|
Large parts, low-to-medium volume, custom designs
|
|
Pressure Forming
|
Combines vacuum + positive air pressure
|
High-precision parts, tight tolerances
|
|
Injection Molding
|
Injects molten plastic into a mold
|
High-volume production, small-to-medium parts
|
|
Blow Molding
|
Uses air pressure to inflate plastic into a mold
|
Hollow parts (bottles, containers)
|
FAQs About Vacuum Forming
Q: What is the maximum size of a part I can vacuum form?
Q: How long does it take to produce a vacuum formed part?
Q: Can vacuum forming be used for food-safe or medical applications?
Q: Is vacuum forming suitable for prototyping?
Q: What is the typical cost of a vacuum forming machine?
Final Thoughts







