How to Choose a Vacuum Forming Machine: A Guide for Startups and Large – Scale Factories
Introduction: Match Machine to Your Production Reality
Part 1: Startups & Small Businesses – Lean, Flexible, Low-Risk
|
Metric
|
Target Range
|
Rationale
|
|
Monthly Production
|
100–10,000 units
|
Avoid overcapacity; match variable demand
|
|
Budget
|
15,000 |
Preserve capital for marketing/product dev
|
|
Footprint
|
≤1.2m²
|
Fit small workshops/co-working spaces
|
|
Mold Change Time
|
≤20 minutes
|
Adapt to multiple custom designs
|
Top Machine Picks for Startups
- Small Desktop Vacuum Forming Machine
- Ideal For: Prototypes, promotional products (e.g., branded display stands), small-batch blister packs.
- Key Specs: Sheet thickness (0.3–1.5mm), manual/semi-automatic operation, compatible with HIPS/PETG (low-cost materials).
- Pro Move: Choose models with detachable heating elements—they’re easier to store and maintain.
- Keyword Fit: “small desktop vacuum forming machine for custom products” “affordable vacuum forming machine for startups”
- Entry-Level Semi-Automatic Vacuum Forming Machine
- Ideal For: Growing startups (5,000–10,000 units/month) producing food packaging or medical samples.
- Key Specs: Automatic feeding/cooling, sheet thickness (0.5–3mm), basic PLC controls (no technical expertise needed).
- Cost-Benefit: Cuts labor time by 40% vs. desktop models while staying under $15k.
- Keyword Fit: “semi-automatic plastic vacuum forming machine” “entry-level vacuum thermoforming machine”
- Steer clear of fully automatic machines (high upfront cost + idle capacity).
- Reject models without clear technical support (you won’t have an in-house team to troubleshoot).
- Skip machines limited to one material—flexibility is critical for custom orders.
Part 2: Large-Scale Factories – Speed, Consistency, Scalability
|
Metric
|
Target Range
|
Rationale
|
|
Monthly Production
|
20,000–500,000+ units
|
Meet mass-market demand
|
|
Cycle Time
|
≤25 seconds/part
|
Maximize throughput
|
|
Thickness Tolerance
|
±0.1mm
|
Ensure consistent product quality
|
|
Compliance
|
CE/ISO/FDA/GMP
|
Meet global industry standards
|
Top Machine Picks for Large Factories
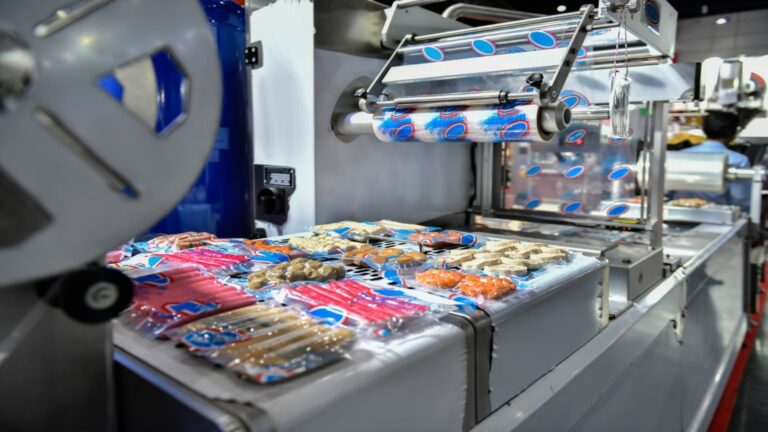
- Fully Automatic Vacuum Forming Machine
- Ideal For: Mass production of food trays, medical containers, or electronic packaging.
- Key Specs: Automatic feeding/trimming/cooling, sheet thickness (0.5–3mm), speed (20–50 parts/min), PLC with recipe storage (for multiple SKUs).
- Must-Have Feature: Integration with robotic stacking systems to reduce labor costs.
- Keyword Fit: “fully automatic vacuum forming machine for food trays” “CE certified vacuum forming machine 0.5-3mm sheet”
- Rotary Vacuum Forming Machine
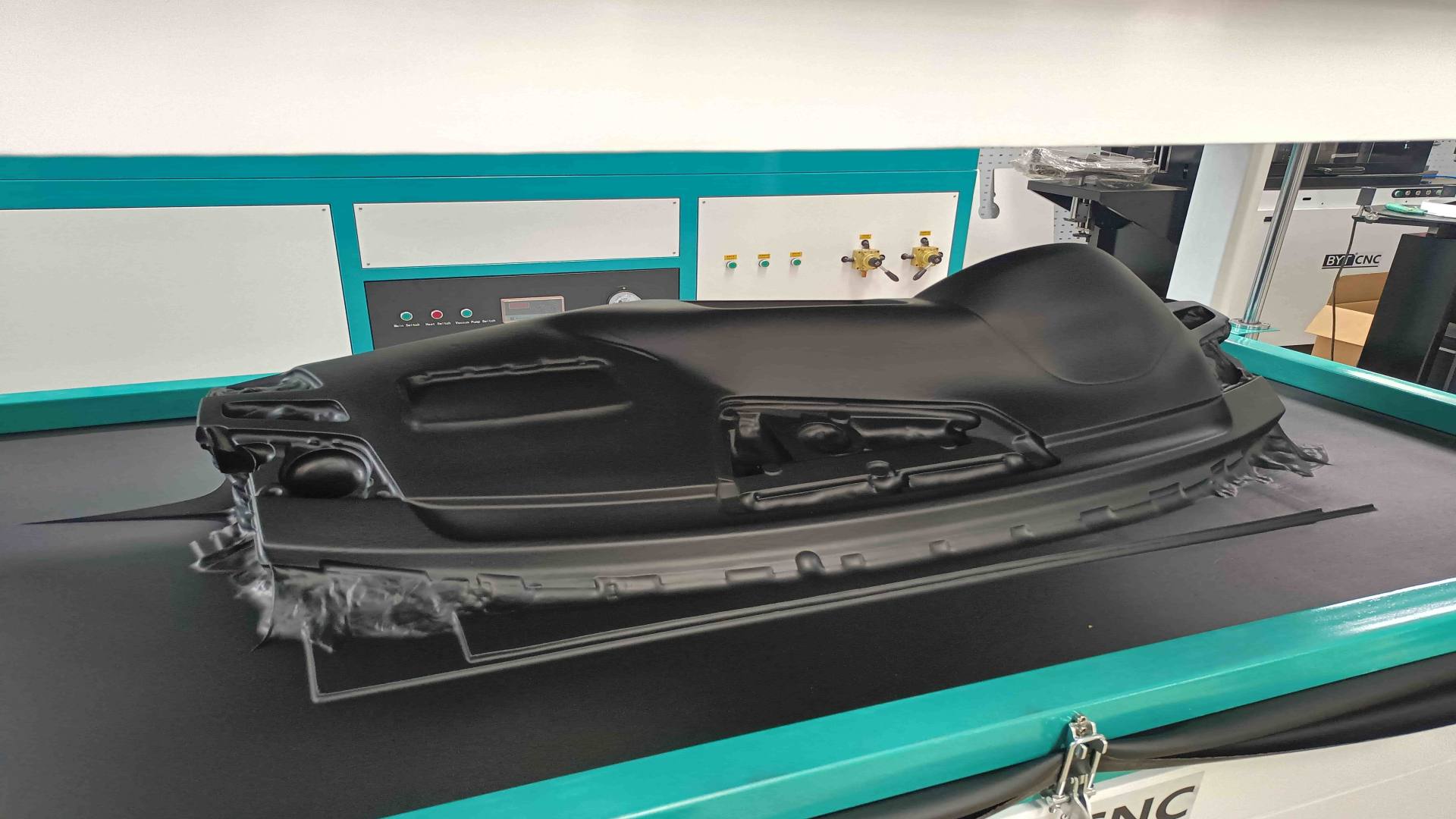
- Ideal For: Continuous production of automotive components, industrial casings, or large packaging.
- Key Specs: Multi-station design (heating/forming/cooling/trimming), sheet thickness (1–10mm), heavy-duty vacuum pump (≥7.5kW), stainless steel frame.
- Efficiency Boost: 30–50% higher output than standard automatic models (no downtime between cycles).
- Keyword Fit: “rotary vacuum forming machine for automotive parts” “heavy-duty plastic vacuum thermoforming machine”
Factory Must-Ask Questions
- Can it integrate with our existing conveyor belts or quality inspection systems?
- What’s the uptime rate? (Aim for ≥98%—even 1% downtime costs $10k+/month for high-volume lines.)
- Does the manufacturer offer on-site training and 24/7 technical support?
Part 3: Universal Tips for Both Sizes – Avoid Costly Mistakes
- Test Before You Buy: Request a sample run with your target material (e.g., PP for food trays, ABS for automotive parts) to verify quality.
- Calculate Total Ownership Cost (TOC): Don’t just look at upfront price—factor in energy consumption, mold costs, and maintenance (durable ceramic heating elements save $500+/year in replacements).
- Prioritize Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine handles your core materials (e.g., FDA-approved plastics for food, flame-retardant materials for electronics).
- Plan for Growth: Startups should choose semi-automatic models upgradable to fully automatic; factories need machines with modular designs (add extra stations as demand grows).